Laden: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(→Leistungsbilanz) |
(→Battery) |
||
| Zeile 28: | Zeile 28: | ||
Insgesamt: 3A * 27V + 1A * 5V = 81W + 5W = 86W | Insgesamt: 3A * 27V + 1A * 5V = 81W + 5W = 86W | ||
| − | = | + | =Akku= |
| − | + | Als Akku wird ein 'Sony Konion 7S2P' Lithium Ion Akkupack ([http://www.repasebaterii.cz/files/img/datasheet/us18650v3.pdf Sony Konion US18650V3 2250 mAh cells, Li-Mn]), 29.4V x 4500 mAh = 132 Wh, 500 Ladezyklen, 126 x 36 x 65 mm (LBH) verwendet. | |
| − | + | Die Mähzeit beträg mit den Ardumower-Motoren ungefähr 1,5 Stunden (132 Wh / 86W). | |
| − | + | Akku Lade-/Entladebedingungen für optimale Lebensdauer: | |
| − | * | + | * Ladeschlussspannung pro Zelle: max 4.15V ( 0.3A - 0.1A Rest-Ladestrom) |
| − | * | + | * minimale Entladespannung: min 3.1V |
=Standby-off / Under-voltage protection= | =Standby-off / Under-voltage protection= | ||
Version vom 14. Juli 2015, 11:55 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Grundprinzip
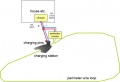
Der Roboter findet seine Ladestation, wo er wieder aufgeladen wird mit Hilfe der Perimeter-Schleife. Er fährt also solange in Uhrzeiger-Richtung an der Schleife entlang bis er eine Ladespannung an den Ladeanschlüssen feststellt. Hier stoppt der Roboter und lädt seinen Akku wieder auf.
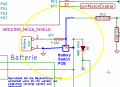
Ladegerät
wir benutzen ein Lithium Ion e-bike Ladegerät (29.4V, 1.5A Ladestrom-Begrenzung) das über den Marotronics-Shop shop ![]() bezogen werden kann . Das Ladegerät wird in einem geschützten Bereich untergebracht (z.B. im Haus) und mit der Ladestation verbunden. Das Ladegerät sollte folgendes leisten( hier für Lithium-Ionen-Zellen, bei Bleiakkus ist es ähnlich aber weniger kritisch):
bezogen werden kann . Das Ladegerät wird in einem geschützten Bereich untergebracht (z.B. im Haus) und mit der Ladestation verbunden. Das Ladegerät sollte folgendes leisten( hier für Lithium-Ionen-Zellen, bei Bleiakkus ist es ähnlich aber weniger kritisch):
- Laden des Akkupacks über dei Ladeanschlüsse des Roboters
- Einhaltung der maximalen Ladespannung (Ladeschluss-Spannung)
- Einhaltung dess maximalen Ladestroms (Ladestrom-Begrenzung)
Wenn du ein vorhandenes Ladegerät benutzt, sind diese Anforderungen mit höchstwahrscheinlich erfüllt.
Leistungsbilanz
- 2 x Getriebemotor jeder 1A (unter Last): 2A, 27V (gemessen mit max. 80% Genauigkeit des Motortreibers)
- 1 x Mähmotor 1A (unter normaler Last): 1A, 27V (gemessen mit max. 80% Genauigkeit des Motortreibers)
- Board: 1A, 5 Volt (nicht gemessen)
Insgesamt: 3A * 27V + 1A * 5V = 81W + 5W = 86W
Akku
Als Akku wird ein 'Sony Konion 7S2P' Lithium Ion Akkupack (Sony Konion US18650V3 2250 mAh cells, Li-Mn), 29.4V x 4500 mAh = 132 Wh, 500 Ladezyklen, 126 x 36 x 65 mm (LBH) verwendet.
Die Mähzeit beträg mit den Ardumower-Motoren ungefähr 1,5 Stunden (132 Wh / 86W).
Akku Lade-/Entladebedingungen für optimale Lebensdauer:
- Ladeschlussspannung pro Zelle: max 4.15V ( 0.3A - 0.1A Rest-Ladestrom)
- minimale Entladespannung: min 3.1V
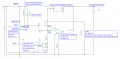
Standby-off / Under-voltage protection
There are two reasons for a battery switch (standby-off mechanism):
Reason1: If the robot was not started within 5 minutes, it should turn battery off to save energy.
Reason2: Modern batteries should not be completely discharged. When the robot isn't able to charge for some reason and when the battery is below a certain threshold, it should be able to switch off the battery itself (undervoltage protection)
Idea:
- User presses existing START/POWER button, that switches on the MOSFET for the time of pressing
- Arduino starts and immediately also switches on MOSFET (via Arduino pinBatterySwitch)
- If undervoltage detected, Arduino switches off MOSFET (via Arduino pinBatterySwitch)
- Emergy button is still used for completely switching ON/OFF power
- POWER/START button: switches-on operation voltage (1st one second press), starts robot in automatic mode (2nd one second press)
BOM: 1x IRF9540N P-MOSFET T1 (or IRF5210) 1x BC337 NPN T2 1x Zener Diode 15V ZD15 Z1 2x Diode 1N4148 D2, D3 2x Diode 1N5819 50V D1, D4 1x 22 uF C1 1x 1k R4 2x 10k (R3, R8) 1x 30k R6 2x 100k (R2, R7)
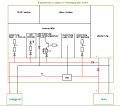
Robot charging
In the robot itself, the battery voltage is monitored (see diagram below). So it can be determined when the robot must go to the charging station. The robot and the voltage and the current during charging is controlled. So it can be determined whether the robot has reached the charger and when the battery is fully charged again.
robot charging circuit:
Robot charging (+)---+------+-- relais ---- current sensor ----- battery (+)
|
---- voltage sensing
Robot charging (-)-- +------------------------------------------ battery (-)
Charging station
Ideally, the charging station also powers the perimeter loop sender.
charging station circuit:
AC power supply => Charger 24V (+)----- Charging station charger pin(+)
GND (-)----- Charging station charger pin(-)
Charger 24V (+)----- DC-DC converter 12V => Perimeter sender MC motor driver
=> Perimeter sender Arduino Nano Vin
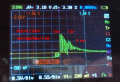
Charge monitoring/Battery settings
Via pfodApp (Android) you can monitor the charging process.
Charging station ideas
Videos