PCB 1.3 (English): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Added chapter "Soldering the Voltage regulator") |
(Added chapters "Soldering the RTC", "Soldering the motor drivers") |
||
| Zeile 359: | Zeile 359: | ||
[[File:Voltage regulator assembly.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator placed on the PCB 1.3|400px]] | [[File:Voltage regulator assembly.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator placed on the PCB 1.3|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Soldering the RTC== | ||
| + | |||
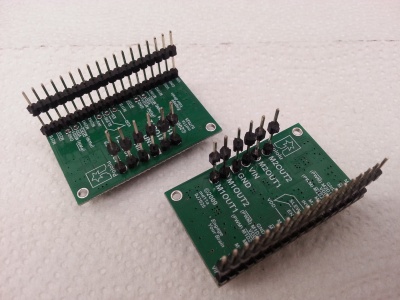
| + | Just insert a 5- and a 7-pin-row into the module. It's pretty easy if you insert the module into the main board while soldering. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Voltage regulator front.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator front view|400px]] | ||
| + | [[File:Voltage regulator back.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator back view|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unplug the regulator and connect a +24 V voltage source to the inputs and a multimeter to the outputs (measure DC voltage). Adjust the output voltage to 9 V using the screw on top of the potentiometer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Voltage regulator calibration.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator calibration using a multimeter|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Plug the voltage regulator into the PCB and make sure the orientation is right! | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Voltage regulator assembly.jpg|none|thumb|Voltage regulator placed on the PCB 1.3|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Soldering the motor drivers== | ||
| + | |||
| + | For each of the both drivers: Insert a row of 18 stacking pins (the longer ones) row into the mainboard. Insert 6 separated stacking pins into the mainboard. Try to put the module onto those pins and solder them. | ||
| + | |||
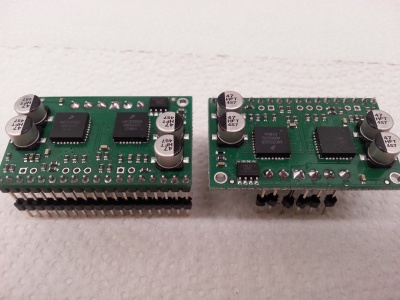
| + | [[File:Motor driver front.jpg|none|thumb|Motor driver front view|400px]] | ||
| + | [[File:Motor driver back.jpg|none|thumb|Motor driver back view|400px]] | ||
=Forum= | =Forum= | ||
http://www.ardumower.de/index.php/de/forum/ardumower-pcb/1348-building-instruction-for-the-1-3-board | http://www.ardumower.de/index.php/de/forum/ardumower-pcb/1348-building-instruction-for-the-1-3-board | ||
Version vom 21. Mai 2018, 21:45 Uhr
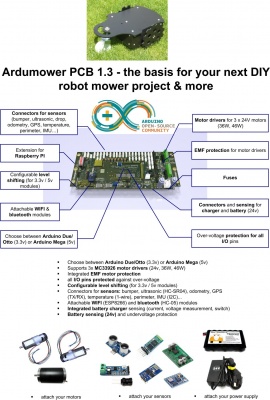
This page describes how to assemble PCB 1.3, how to add modules and how to configure the PCB. The PCB and all required modules can be purchased as complete kits via the shop ![]() .
.
NOTE: WE ARE CURRENTLY WORKING ON THIS PAGE - PLEASE LOOK AT PCB 1.2 FOR MISSING INFORMATION
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Specifications
PCB size: 272mm x 115mm
Schematics, Drawings, Photos
Videos
- Assembly part 1 (jumper, capacitors (power), INA, jumper power, bargraph, bluetooth, jumper I2C bus)
- Assembly part 2 (motor drivers)
- Assembly part 3 (Arduino, protection, MOSFET, fuse holder, relay)
- Assembly part 4 (back side: odo-divider, power connectors, buzzer, resistors, capacitors)
- Assembly part 5 (sensor jumpers, connector sockets)
- Assembly part 6 (Capacitors motor output stage )
- Assembly part 7 (Placing into operation)
Checklist
- only set jumper JP1 (9V power) after you have manually set and measured the correct voltage (9v) at DC/DC Vout pin
- set jumper JP13 on PCB back side for a Marotronics Arduino Due (i.e. Due clone) for automatic reset
- set jumper JP12 (GPS signal voltage) to 3.3VP for Marotronics GPS module
- set jumper JP7 (GPS operating voltage) to 5VP for Marotronics GPS module
- set jumper JP10 (Bluetooth signal voltage) to 3.3VP for Marotronics Bluetooth module
- set jumper JP4 (Bluetooth operating voltage) to 5V for Marotronics Bluetooth module
- set jumper JP6 (WIFI operating voltage) to 3.3V for Marotronics WIFI module
- set jumper JP11 (WIFI signal voltage) to 3.3V for Marotronics WIFI module
- set jumper JC2 (IMU signal voltage) to 3.3V for Marotronics IMU module
- only set I2C jumpers JC2, JC3, JC4, JC5, JC6, JC7 (at the top) if there is a corresponding I2C module installed
- set jumper JP8 to 'Always-ON' for tests and for Arduino uploads, for regular operation (and automatic undervoltage power-off) to 'Automatic'
- unset jumper JP3 (2nd mower motor MC33926 M1FB), not used
- Solder a bridge on leftmost pins of S1 ODO right and S2 ODO left (PCB back side)
- RTC module must be installed for proper I2C bus operation
- press button P20 to power-on PCB
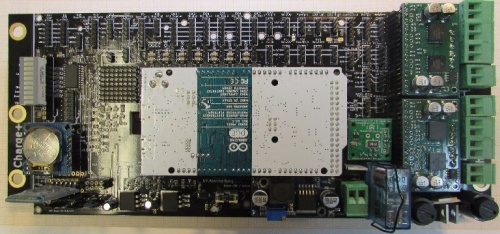
Assembly
Soldering the mainboard components
The assembly of the board is tricky as some components have been packed tightly - especially those below the motor drivers.
The following table lists each component to be placed by hand along with other components that might collide. Collisions marked with a '?' are hard (but still possible) to solder if the components are not placed in the right order. Those without a '?' are impossible. The table has been sorted to provide a practical order for soldering: low components come first and components blocking each other are in the right order. Similar components and spatiality has been used to form groups.
| Component | Can be blocked by | Can block | Profile | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3 | P22, P4 | low | SMD | |
| F1 | JP1?, C1? | low | SMD | |
| S1 | low | solder a small lead as bridge | ||
| S2 | low | solder a small lead as bridge | ||
| S3 | low | solder a small lead as bridge | ||
| C2 | low (lying) | |||
| C3 | low (lying) | |||
| C9 | low | Wasn‘t included. Maybe optional? | ||
| C12 | low (lying) | |||
| D10 | K3 | low | ||
| I2C1 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C2 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C3 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C4 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C5 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C6 | low | connector socket | ||
| I2C7 | low | connector socket | ||
| P1 | C11? | low | connector socket | |
| P2 | C11? | low | connector socket | |
| P3 | low | connector socket | ||
| P4 | JP3 | low | connector socket | |
| P5 | low | connector socket | ||
| P6 | low | connector socket | ||
| P8 | SP1 | SP1? | low | connector socket |
| P9 | low | connector socket | ||
| P11 | low | connector socket | ||
| P12 | low | connector socket | ||
| P13 | low | connector socket | ||
| P14 | low | connector socket | ||
| P19 | C11? | low | connector socket | |
| P20 | C10? | low | connector socket | |
| P21 | C11? | low | connector socket | |
| P22 | JP3 | low | connector socket | |
| P23 | low | connector socket | ||
| P25 | low | connector socket | ||
| P26 | low | connector socket | ||
| P27 | low | connector socket | ||
| P28 | low | connector socket | ||
| P30 | low | connector socket | ||
| P31 | C10? | low | connector socket | |
| P35 | low | connector socket | ||
| P40 | low | connector socket | ||
| P41 | C11? | low | connector socket | |
| P44 | low | connector socket | ||
| P46 | SP1, C11? | SP1? | low | connector socket |
| P48 | low | connector socket | ||
| P7 | low | socket | ||
| P10 | low | socket | ||
| U1 | low | socket | ||
| U2 | low | socket | ||
| U3 | C10? | low | socket | |
| U8RTC | low | socket? | ||
| U11 | low | socket | ||
| JC2 | mid | pins | ||
| JC3 | mid | pins | ||
| JC4 | mid | pins | ||
| JC5 | mid | pins | ||
| JC6 | mid | pins | ||
| JC7 | mid | pins | ||
| JP1 | F1? | mid | pins | |
| JP2 | mid | pins | ||
| JP4 | mid | pins | ||
| JP5 | mid | pins | ||
| JP6 | mid | pins | ||
| JP7 | mid | pins | ||
| JP8 | mid | pins | ||
| JP9 | mid | pins | ||
| JP10 | mid | pins | ||
| JP11 | mid | pins | ||
| JP12 | mid | pins | ||
| JP13 | mid | pins | ||
| P24 | mid | pins | ||
| P29 | mid | pins | ||
| P32 | mid | pins | ||
| P33 | mid | pins | ||
| P34 | mid | pins | ||
| P38 | mid | pins | ||
| P45 | mid | pins | ||
| P47 | mid | pins | ||
| P50 | mid | pins | ||
| P51 | mid | pins | ||
| BY1 | PRFA2? | RL1? | low | |
| BY4 | PRFA2? | low | ||
| BY7 | CC2? | low | ||
| DKE1 | CC2, RL2? | low | ||
| BY8 | CC2, RL2? | low | ||
| BY9 | PRFA1?, C10? | low | ||
| BY10 | PRFA1?, CC3, RL3? | CC3? | low | place in a raised position |
| RL3 | C10, BY2, BY11, PRFA1? | BY2?, BY10?, BY12? | low | |
| PRFA2 | RL1, C11? | BY1?, BY3?, BY4? | low (lying) | lay down later |
| RL1 | BY3, DKE2, BY1?, C11? | PRFA2 | low | |
| BY3 | PRFA2? | RL1 | low | |
| PRFA1 | RL2 | RL2?, RL3?, BY9?, BY10?, BY12?, C10?, EF3? | low (lying) | lay down later |
| RL2 | P49, BY6, BY5, PRFA1? | BY8?, DKE1?, PRFA1 | low | |
| EF3 | PRFA1?, CC3 | CC3 | low | Conflict CC3 |
| CC3 | EF3, BY12, BY10? | EF3, BY10 | high | Conflict EF3 |
| BY2 | C11?, RL3? | RL3 | low | |
| BY5 | CC2? | RL2 | low | |
| BY6 | P49 | RL2 | low | |
| BY12 | RL3?, PRFA1? | CC3 | low | |
| BY11 | C11? | RL3 | low | |
| DKE2 | C11? | RL1 | low | |
| Dual1 | C10 | C10? | low | socket; solder the sockets near the screw connectors later |
| Dual2 | C11 | C11? | low | socket; solder the sockets near the screw connectors later |
| K3 | D10 | mid | relais socket | |
| Due | C10? | high | high pins; insert them into the Due-board first and then place them alltogether into the mainboard for soldering | |
| SP1 | P8?, P46? | P8, P46 | mid | Speaker; alternatively placed at SP2 |
| SP2 | mid | Speaker; alternatively placed at SP1 | ||
| C10 | PRFA1?, Dual1? | Dual1, Due?, P31?, RL3, U3?, BY9? | high (lying) | Hot glue the capacitor to the mainboard for mechanical stability |
| C11 | Dual2? | DKE2?, Dual2, P1?, P2?, P19?, P21?, P41?, P46?, PRFA2?, RL1?, BY2?, BY11? | high (lying) | Hot glue the capacitor to the mainboard for mechanical stability |
| P15/P16/P18 | high | screwed connector socket | ||
| P17/P39/P36 | high | screwed connector socket | ||
| P37 | high | screwed connector socket | ||
| P42 | high | screwed connector socket | ||
| P43 | high | screwed connector socket | ||
| P49 | EF1? | RL2, BY6 | high | screwed connector socket |
| C1 | F1? | high (upright) | ||
| C8 | high (upright) | |||
| C13 | high (upright) | |||
| CC1 | high | |||
| CC2 | DKE1, BY5?, BY7?, BY8? | high | ||
| D1 | high | |||
| D9 | high | |||
| D73 | high | |||
| Q2 | high | |||
| Q4 | high | |||
| EF1 | P49? | very high | ||
| EF2 | very high |
Soldering the Voltage regulator
Just insert four 1-pins into the corners. It's pretty easy if you insert the module into the main board while soldering.
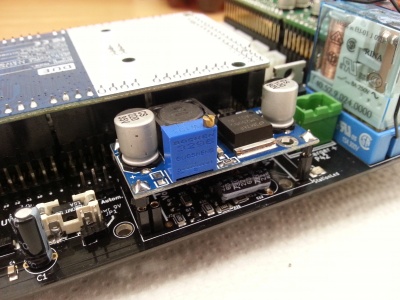
Unplug the regulator and connect a +24 V voltage source to the inputs and a multimeter to the outputs (measure DC voltage). Adjust the output voltage to 9 V using the screw on top of the potentiometer.
Plug the voltage regulator into the PCB and make sure the orientation is right!
Soldering the RTC
Just insert a 5- and a 7-pin-row into the module. It's pretty easy if you insert the module into the main board while soldering.
Unplug the regulator and connect a +24 V voltage source to the inputs and a multimeter to the outputs (measure DC voltage). Adjust the output voltage to 9 V using the screw on top of the potentiometer.
Plug the voltage regulator into the PCB and make sure the orientation is right!
Soldering the motor drivers
For each of the both drivers: Insert a row of 18 stacking pins (the longer ones) row into the mainboard. Insert 6 separated stacking pins into the mainboard. Try to put the module onto those pins and solder them.
Forum
http://www.ardumower.de/index.php/de/forum/ardumower-pcb/1348-building-instruction-for-the-1-3-board