IMU: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(→IMU module GY-80) |
(→Assembly) |
||
| Zeile 40: | Zeile 40: | ||
==Assembly== | ==Assembly== | ||
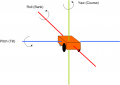
This photo shows how the IMU module is placed in driving position (the black arrow shows the driving position). The shown tube was a prototype. Actually, you can now place the IMU module directly in the robot. | This photo shows how the IMU module is placed in driving position (the black arrow shows the driving position). The shown tube was a prototype. Actually, you can now place the IMU module directly in the robot. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File: Gy80_direction.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==Calibration (v0.9.3)== | ==Calibration (v0.9.3)== | ||
Version vom 12. September 2014, 09:27 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Abstract
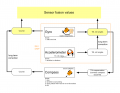
An IMU (Intertial Measurement Unit) is key component of an intertial navigation system. We use it to:
- detect if the robot is in tilt orientation
- keep the robot on track for the 'lane-by-lane' mowing pattern
Acceleration sensor
An acceleration sensor measures earth gravity force (m*s^2) in all 3 robot axes (x/y/z) allowing you to calculate the orientation towards earth center of the robot (Roll, Pitch). However, it cannot detect movement around Yaw - this requires a gyro.
Gyro
A gyro measure rotation speed (degree/second) in all 3 robot axes (Rol, Pitch, Yaw). This allows us to correct the robot if it is driving 'off-course' due to wet conditions or slope.
Compass
If a robot drives on a wet lawn, you'll notice quickly that it will not drive straight forward, but instead tends to drive into the direction of the slope. A compass can solve this problem and the robot will drive again straight forward.
However, a compass has a problem: if tilting the robot, the compass measurements (x,y,z) relate to the tilted robot. So, you need to correct them using knowing the tilt angles. This requires the use of the accerlation sensor (x,y).
Sensor fusion
To eliminate the issues of all sensor, they are merged to compute the course (degree) and pitch/roll angles.
We use a complementary filter to fusion all sensor values.
IMU module GY-80
- Acceleration sensor: ADXL345B
- Compass sensor: HMC5883L
- Gyro: L3G4200D
- Pressure sensor: BMP085 (not used here)
Assembly
This photo shows how the IMU module is placed in driving position (the black arrow shows the driving position). The shown tube was a prototype. Actually, you can now place the IMU module directly in the robot.
Calibration (v0.9.3)
Acceleration sensor
Compass sensor
Calibration (SVN version)
Acceleration sensor
Jede der 6 Seiten des Moduls einmal exakt hochkant hinstellen, nicht bewegen und den Punkt zur Kalibrierung der nächsten Seite auswählen:
- In der seriellen Konsole "IMU acc calibration next side" oder
- In der pfodApp "Settings->IMU->acc calibration next side"
Während der Messung einer Seite das Modul nicht bewegen! Die Messung wird begleitet von einem kurzen Ton.
Diesen Schritt für alle 6 Seiten wiederholen. Wenn alle 6 Seiten kalibriert wurden, ertönt ein kurze Melodie.
Compass sensor
Modul außer Reichweite von magnetischen oder eisenhaltigen Quellen bringen! Kompaß-Kalibrierung starten:
- In der seriellen Konsole "IMU com calibration start/stop" oder
- In der pfodApp "Settings->IMU->com calibration start/stop"
Jede der 6 Seiten des Moduls einmal Richtung Norden halten und das Modul solange kippen bis sich das Minimum und Maximum der Achsen nicht mehr ändert (kein Ton mehr ausgegeben wird):