Chassis (English): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
FelixP (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Case assembly) |
FelixP (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Case assembly) |
||
| Zeile 71: | Zeile 71: | ||
[[File:20180126 115445.jpg]] | [[File:20180126 115445.jpg]] | ||
| − | We start with the bottom, right and left board | + | We start with the bottom, right and left board. You have to see you remove all the remaining plastic from the notch in the bottom board. Otherwise the side boards will not fit into it. |
[[File:BottomAndSides.jpg]] | [[File:BottomAndSides.jpg]] | ||
Version vom 23. Juni 2020, 22:12 Uhr
This page describes the assembly of the Ardumower chassis that you can purchase via the shop ![]() .
.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
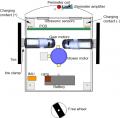
Ardumower 1.0 Chassis specifications
- Dimension (L/B/H): 60x36x25cm
- Total weight: approx 9 kg (including all components - motors, battery, PCB etc.)
- Adjustable mower motor height
- Mowing motor: 24V DC, 3150 rpm, 140 mNm, 46W
- Mowing disc: 190mm diameter, 3 blades
- Wheels: 250mm diameter
- Free wheel: 125mm diameter
- Gear motors: 2 x DC 24V planetary drive, 31 rpm, 2.45 Nm, 8mm shaft, with integrated encoders
- A rotation speed up to 31 rpm allows to move the robot at sufficient speed (at up to meter/sec = 31rpm/60 * PI * 0.25m = 0.4m/sec using 250mm diameter wheels)
- A high torque (2.45Nm) guarantees that the robot can climb small hills as well (with 2 motors, 0.125 radius wheel, 31rpm = 0.4m/s, acceleration = 0.2 ( 1/2 of nominal speed) see calculator
- Integrated encoders, so it can measure the rotation speed and the distance
- Battery: Lithium-Ion 29.4V
- Max. incline: approx. 30%
- Material: PE-HD plates (8mm) and alumnium profiles
Videos
- Ardumower at Berlin Maker Faire 2019 (Source: "hallo deutschland")
- Building an Ardumower: chassis, motors, tires assembling
- Building an Ardumower: chassis, motors, tires assembling (slow)
- Overall impression
- Loundness test
- Gear motor test
- Gear motor hardness test
- Mowing motor hardness test
- Perimeter wire test (indoor)
- Perimeter wire test (120m outdoor)
- Obstacle detection via motor current
- Obstacles detection via ultrasonic
- Robot releases itself
- Robot releasing long-time test
- Plastic blades test
- Docking test (very initial prototype)
- Rain sensor test
- 3D simulation
Assembly
Required Tools
- Screw driver
- Different Imbus screw driver
- Different Torx screw driver
Optional Tools
- Round and flat file
- Electric padsaw
- Drill machine with drill set (3,4,6,8,10 mm drills)
Optional Material
- M4 washer and spring washer
Case assembly
This assembly instruction is work in progress!
We recommend to smooth all parts and remove all edges with a file and/or sand paper.
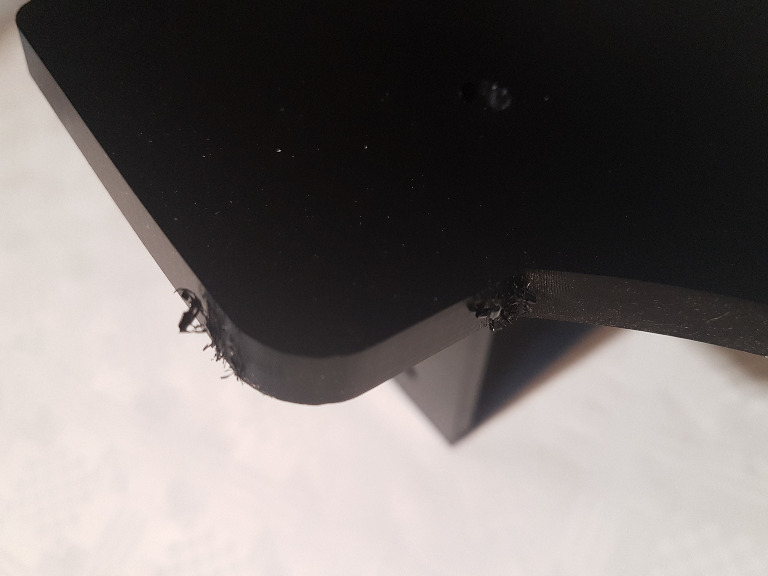
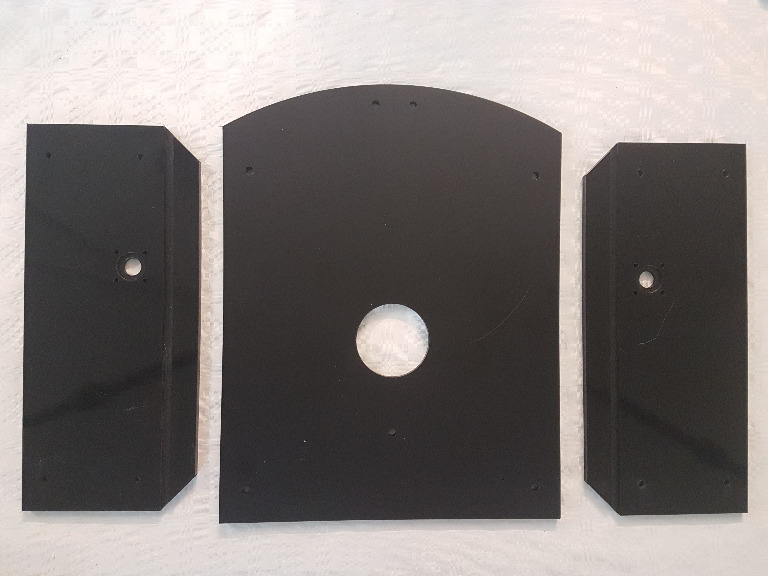
We start with the bottom, right and left board. You have to see you remove all the remaining plastic from the notch in the bottom board. Otherwise the side boards will not fit into it.
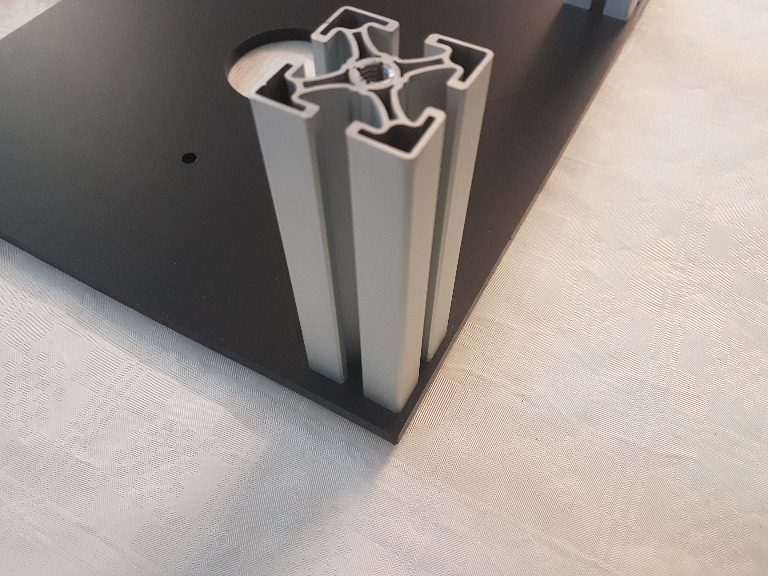
Then we take the bottom board and attach the first aluminium corner. It has the advantage to use the polished polished side of the bottom board downside that the grass sticks to it less well as to the matte side.
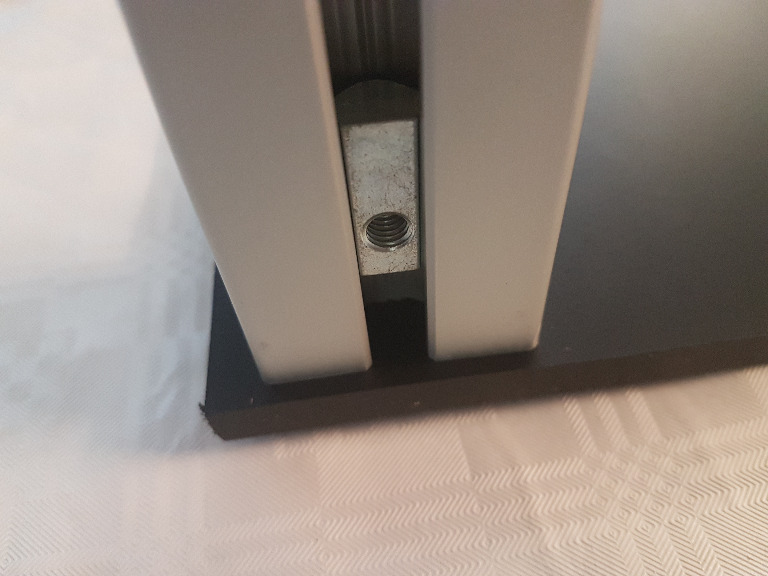
Then we put two M6 nut bolts into the corners.
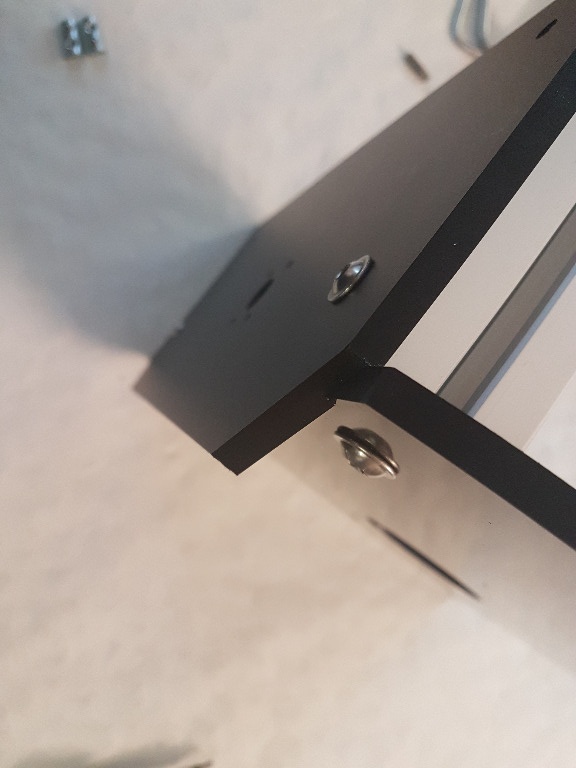
In the next step, we attach the left and right side to the bottom board and fix them with the four M6 screws
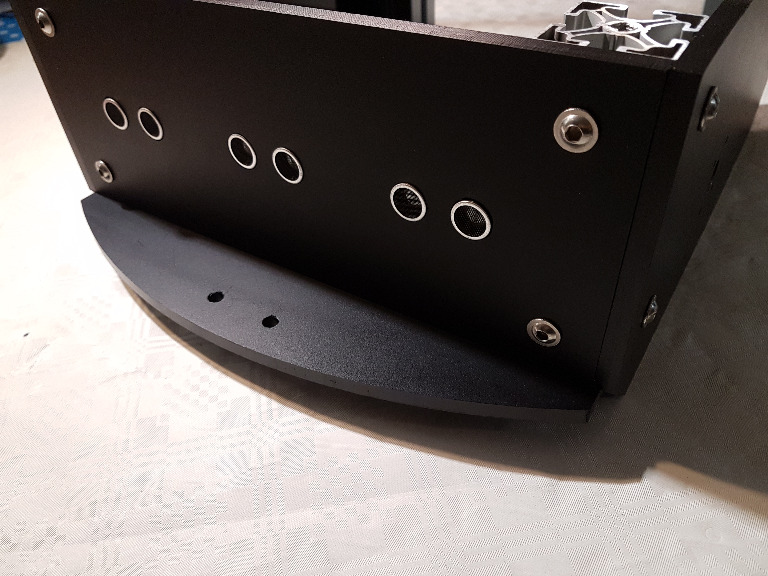
Then we take the front board. If you already know that you want to use the use ultrasonic collision detection, then remove the remaining plastic from the prepared six holes. Use again four M6 screws and the corresponding nuts and attach them between the right and left side of the chassis.
Gear motors
It is recommended to use washers and spring washers to prevent that the screw become unfastened.
Tires
It is recommended to use washers and spring washers to prevent that the screw become unfastened.