Charging: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | + | =Basic principle= | |
About an induction loop, the robot finds the charging station where he can be charged again. In this case, as long as the induction loop traversed (clockwise) to the charging contacts of the robot detect a voltage (charging voltage). There, the robot stops. | About an induction loop, the robot finds the charging station where he can be charged again. In this case, as long as the induction loop traversed (clockwise) to the charging contacts of the robot detect a voltage (charging voltage). There, the robot stops. | ||
| Zeile 7: | Zeile 7: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | =Charger= | |
The charger is in the cradle (or is connected to). The charger should accomplish the following things (in this case lithium-ion - Battery Lead is similar, but less critical): | The charger is in the cradle (or is connected to). The charger should accomplish the following things (in this case lithium-ion - Battery Lead is similar, but less critical): | ||
| Zeile 15: | Zeile 15: | ||
If you are using an existing charging station, these things were implemented with high probability already there. | If you are using an existing charging station, these things were implemented with high probability already there. | ||
| − | + | =Robot= | |
In the robot itself, the battery voltage is monitored (see diagram below). So it can be determined when the robot must go to the charging station. The robot and the voltage and the current during charging is controlled. So it can be determined whether the robot has reached the charger and when the battery is fully charged again. Ideally, the charging station also eat the loop transmitter: | In the robot itself, the battery voltage is monitored (see diagram below). So it can be determined when the robot must go to the charging station. The robot and the voltage and the current during charging is controlled. So it can be determined whether the robot has reached the charger and when the battery is fully charged again. Ideally, the charging station also eat the loop transmitter: | ||
| Zeile 36: | Zeile 36: | ||
| − | ==Charging station ideas | + | =Charge plotting= |
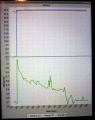
| + | Via pfodApp (Android) you can get a plot of the charging process. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File: Ardumower_battery_plotting.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Charging station ideas= | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File: L50_laden.jpg | File: L50_laden.jpg | ||
| Zeile 44: | Zeile 50: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | + | =Videos= | |
#[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=02REEUf99hI Driving into charging station] | #[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=02REEUf99hI Driving into charging station] | ||
#[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfY6bBFdxYk Drive in and out] | #[http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfY6bBFdxYk Drive in and out] | ||
#[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NLv-mXDqVQU&feature=youtu.be Tracking and docking] | #[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NLv-mXDqVQU&feature=youtu.be Tracking and docking] | ||
Version vom 12. September 2014, 22:39 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Basic principle
About an induction loop, the robot finds the charging station where he can be charged again. In this case, as long as the induction loop traversed (clockwise) to the charging contacts of the robot detect a voltage (charging voltage). There, the robot stops.
Charger
The charger is in the cradle (or is connected to). The charger should accomplish the following things (in this case lithium-ion - Battery Lead is similar, but less critical): Load battery pack via the charging pins of the robot -Maximum Cutoff voltage / charge voltage compliance (charging voltage limit) -Maximalen Charging current compliance (charging current limit) If you are using an existing charging station, these things were implemented with high probability already there.
Robot
In the robot itself, the battery voltage is monitored (see diagram below). So it can be determined when the robot must go to the charging station. The robot and the voltage and the current during charging is controlled. So it can be determined whether the robot has reached the charger and when the battery is fully charged again. Ideally, the charging station also eat the loop transmitter:
charging station circuit:
Power supply => Charger 24V (+)----- Charging station charger pin(+)
GND (-)----- Charging station charger pin(-)
Charger 24V (+)----- DC-DC converter 5V => Perimeter sender Arduino Nano
Charger 24V (+)----- DC-DC converter 12V => Perimeter sender MC motor driver
robot charging circuit:
Charging station (+)---+------+-- relais ---- current sensor ----- battery (+)
|
---- voltage sensing
Charging station (-)-- +------------------------------------------ battery (-)
Charge plotting
Via pfodApp (Android) you can get a plot of the charging process.