Motor driver: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(→Motor Methods) |
(→Programming) |
||
| Zeile 88: | Zeile 88: | ||
File: Odometry_motor_pid_controller.png | File: Odometry_motor_pid_controller.png | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Version vom 30. Mai 2016, 09:33 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Abstract
Ardumower uses two different types of motors (all motors can be purchased via the shop ![]() ):
):
- Two motors (with integrated gearing) for driving (wheel motors) with integrated encoders (for distance and speed control)
- One motor (with high rotation speed) for mowing (mower motor)
To control the motors, it requires motor drivers. In addition, the motor driver measures the motor current, and allows us to detect obstacles as motor current increases at obstacles. Ardumower uses two dual MC33926 motor drivers, so two channels for left and right motor and two dual channels (connected in parallel) for the mowing motor.
Voltages
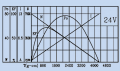
Although there exist 12V motors and 24V motors, as in all modern systems, the Ardumower uses 24V motors.
Wheel motors
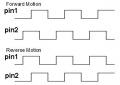
The two left and right gear motors are controlled independently (aka 'differential driving') to:
- drive the robot forward/backward
- steer the robot left/right
The Ardumower wheel motor features:
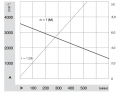
- A rotation speed up to 31 rpm allows to move the robot at sufficient speed (at up to meter/sec = 31rpm/60 * PI * 0.25m = 0.4m/sec using 250mm diameter wheels)
- A high torque (2.45Nm) guarantees that the robot can climb small hills as well (with 2 motors, 0.125 radius wheel, 31rpm = 0.4m/s, acceleration = 0.2 ( 1/2 of nomeinal speed) up to 14 degree) see calculator
- Integrated encoders, so it can measure the rotation speed and the distance
- 24V (load current ~1A)
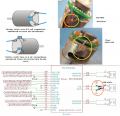
Motor driver (dual MC33926)
Features: up to 3A with integrated current sensor and thermal shut-down protection
![]() Protector board is adviced to be used between controller and motor
Protector board is adviced to be used between controller and motor
Motor wiring (left motor):
black ==== MC33926 M1OUT1 red ==== MC33926 M1OUT2
Odometry wiring (left motor):
brown ---- PCB VCC green ---- PCB GND blue ---- PCB OdometryLeft (3) purple ---- PCB OdometryLeft (4)
For right motor, use MC33926 M2OUT(1,2) and PCB OdometryRight accordingly.
IMPORTANT: PCB v0.5/1.2 are missing pull-ups! You need to add them yourself:
odometry(3) --- 4.7k --- 5v odometry(4) --- 4.7k --- 5v
Mower motor
The Ardumower mower motor features:
- Fast enough to cut the lawn (3150 rpm)
- Enough torque (140 mNm / 46 W)
- Quiet mowing (you cannot hear it)
- 24V, load current ~1.0A (L=2.8mH, R=1.9ohm)
![]() Security note: For security reasons, always remove mower blades in your first tests!
Security note: For security reasons, always remove mower blades in your first tests!
Motor wiring (mower motor):
black ==== MC33926 M1OUT1 red ==== MC33926 M1OUT2
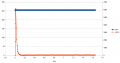
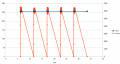
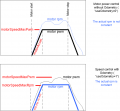
Motor controller (PID)
The speed of the motors is controlled by a software PID controller. You can monitor the quality of the motor speed control via pfodApp (Plot->Motor control):